The ComboBox control is another type of input box. It combines features of a TextBox and a ListBox. We can enter a value (as with the TextBox – see here), or select an existing value from the drop-down. In that case, we need to populate the combo with a list of values first. The ComboBox has most properties and events of a TextBox and a few more. Additionally, the ComboBox has some methods to add and remove items in the box. The toolbox symbol for a ComboBox control is highlighted in the image below.
ComboBox properties
As with other
controls, the Name property is used as an object to target any other property
or method. We can change the default name of the ComboBox control in the
properties window.
The ComboBox has most
properties of a TextBox control (and other controls) and a few more. As with
most controls, we can set the color of the box, borders, font size and style,
position, size, visibility, etc. We can
also align the text (TextAlign) and limit the number of characters added if
manually entered with MaxLength (as with the TextBox). We get or set the value
in a combo box with Value or Text, exactly in the same way done with a text box
(see more about that in the previous page – TextBox). However, we need to use
other properties or methods of the ComboBox to add values to the drop-down list (see
later).
Additionally, the ComboBox has unique properties (most shared
also with the ListBox control) to determine how the input has to match the list
(MatchEntry), change settings for the button (ShowDropButtonWhen) or whether to
display drop-down items as values or options with ListStyle.
Another specific
property of the ComboBox control (and ListBox) is the property List. It allows
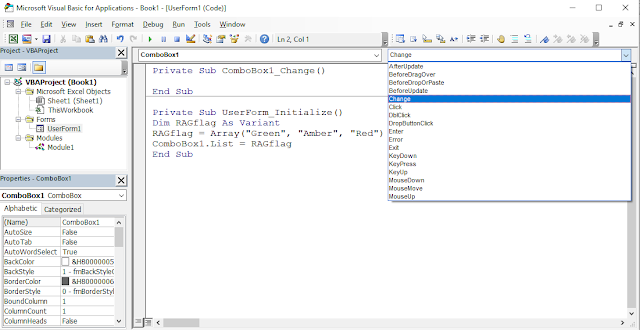
to add a list or array of values to the combo box. The example below populates
the combo box with three values (RAG status) before the userform opens.
ComboBox1.List = Array("Green", "Amber", "Red")
End Sub
Along with List, other
useful properties of the ComboBox are the properties ListCount and ListIndex.
ListCount returns the total number of items in the box while ListIndex returns
the index of the selected item (zero-based).
ComboBox methods
The ComboBox control (and
also ListBox) have two methods to add and remove entries in the box: AddItem
and RemoveItem. They are often used to add and remove items at run-time, like
when adding and deleting data from a database. AddItem could also be used to
populate the combo box before the userform opens (as done earlier with the
property List). An example where the AddItem method may be more convenient to
use than the List property is when adding many values such as the days of the
month.
For d = 1 To 31
ComboBox1.AddItem d
Next d
ComboBox2.List = Application.GetCustomListContents(4)
'...
This other example updates
the possible values for RAG status and adds a new entry in a combo box (from
example above) when clicking a button (CommandButton1). This operation can only
be done with the AddItem method.
ComboBox1.AddItem "New status"
End Sub
ComboBox events
The ComboBox control
has the same events of the TextBox (with one exception – Click) and the ListBox
too. Most used events are those that trigger when changing the value in the box
(Change, BeforeUpdate, Afterupdate). But Change is triggered while typing into
the box (after adding or removing a single digit), while BeforeUpdate or
AfterUpdate occur once the value has been entered by either clicking Return or
selecting other control in the form. The Click event occurs when clicking or
selecting a value in the drop-down and follows after the Change event.
The example below reacts
when selecting a value in a combo box and performs the corresponding action.
For example, when the RAG status is red, it prompts a message and then calls
another macro to take action. The code is added to the event procedure just for
demonstration purposes. However, it should rather go into a macro in a standard
module, being called from the event procedure in the userform module.
MsgBox "Red project - prompt action"
'call macro to execute action
ElseIf RAGstatus = "Amber" Then
MsgBox "Amber project - keep on watch"
Else
'do nothing
As with the TextBox,
we can also control the input with key-stroke events such as KeyDown, KeyPress,
and KeyUp (see more about that in the previous page – TextBox). In the next chapter
we look at the ListBox control, which has a lot of things in common with the
ComboBox.















No comments:
Post a Comment